GUIDE
What is EHS Risk Management in 2023?
EHS risk management is a way to identify potential safety and environmental hazards and minimize their impact on your company. In this guide, we’ll look at some of the challenges organizations face when it comes to risk management, and the tools available to help you meet those challenges.

EHS Risk Management
Risk has always been a part of doing business.
However, many of the risks organizations face today — such as cyberattacks, resource scarcity, and natural disasters due to climate change — didn’t exist or were barely acknowledged a few decades ago.
The risks organizations face today have changed and so have the tools used to identify and manage those risks. Keeping a log of risks in a spreadsheet is no longer the best way to get ahead of potential issues.
That’s why we created this EHS risk management guide.
Table of Contents:
What is EHS risk management?
Why is EHS risk management important?
What are the types of EHS risk?
What is EHS risk assessment?
What is the 5-step risk assessment procedure?
What is a risk register?
What is risk management software?
Next steps & additional resources
(If you’re looking for information about Lisam’s risk management software, visit our risk management software page.)
-
01
Improve risk visibility by identifying “hidden risks” within your organization
-
02
Reduce costs by dealing with business threats before they arise, rather than allowing them to develop into bigger problems
-
03
Make informed decisions based on quantitative risk data, rather than guesswork or a “gut feeling”
-
04
Demonstrate compliance and continuous improvement in relation to current and future regulations
-
05
Increase shareholder confidence by lowering the company’s risk profile
-
06
Gain a competitive advantage by operating efficiently
Benefits of a Proactive Approach to EHS Risk Management
What are the Types of EHS Risk?
Most of the time when we’re talking about EHS risk management, we think of safety risks. You’re probably familiar with job hazard assessment (JHA), which is one way of identifying safety risks related to a specific task or activity.
But safety is only one facet of EHS risk. EHS risk management encompasses many different types of risk across your enterprise. Often, these risks span many departments (finance, HR, operations) and activities — which is what makes managing these risks so challenging.
Here are a few common types of EHS risk:
Compliance risk: Potential exposure to fines, legal penalties, and losses when a company fails to comply with laws and regulations
Example: A company receives a serious OSHA violation for failing to use proper fall protection.
What is EHS Risk Assessment?
An EHS risk assessment is a formal process to identify potential environmental, health and safety hazards related to your organization’s operations. Conducting an EHS risk assessment can help you determine which risks pose the greatest threat to your operations, and identify controls to reduce the level of risk.
You should conduct a risk assessment any time a hazard is identified, or there’s a change to your operations that could introduce new risks.
Since there are so many different types of EHS risk, EHS risk assessments can vary widely in scope. Here are a few well-known types of risk assessment:
- JHA
- JSA
- Environmental risk assessment
- Climate risk assessment
Next, let’s look at the steps to conduct an effective EHS risk assessment.
1. Identify Hazards
A hazard is anything that has the potential to cause harm to people, property, or processes. This includes everything from heavy machinery to chemicals, electricity, working alone, or even driving.
Some hazards can be identified simply by taking a thorough look at the worksite. However, other hazards — especially non-routine situations like maintenance or cleaning — may be more difficult to observe. In that case, talking to workers who are familiar with the task or facility, asking lots of questions, and capturing employee observations can help you to identify potential hazards you might otherwise have overlooked.

2. Determine Who Might be Harmed and How
As you identify hazards, you’ll need to think about the possible consequences of each hazard. For example, if you’ve identified improperly stored chemicals as a hazard, some of the possible consequences might be:
- Chemicals could degrade
- Workers or cleaning staff can be exposed to a hazardous substance
- Leaks or spills
- Fire or explosion
It’s important to remember that risk assessments not only cover hazards to employees, but to anyone who might be impacted by your operations. Subcontractors, maintenance and cleaning personnel, customers, visitors, the community, and the environment will all need to be carefully considered during the risk assessment. For example, an accidental release of chemicals could impact not only your operations but also the local air or water supply.

3. Evaluate & Prioritize
Next, you’ll need to determine the level of risk related to each hazard you’ve identified. Some risks — like the risk of a chemical explosion — are very severe but very unlikely to occur. Other risks may have less potential for harm, but be more likely to occur.
It doesn’t always make sense to implement controls for every single risk you’ve identified — nor would it be feasible to do so. Instead, you’ll need to focus your efforts on those risks that are most severe and most likely to occur.
One way to determine which risks are most serious and therefore need controls is by using risk scoring. Risk scoring is the process of assigning a numerical value to a risk depending on its severity and the likelihood that it will occur. Scoring gives you an objective way to compare and prioritize risks across your organization. Here’s an example of a risk scoring matrix:

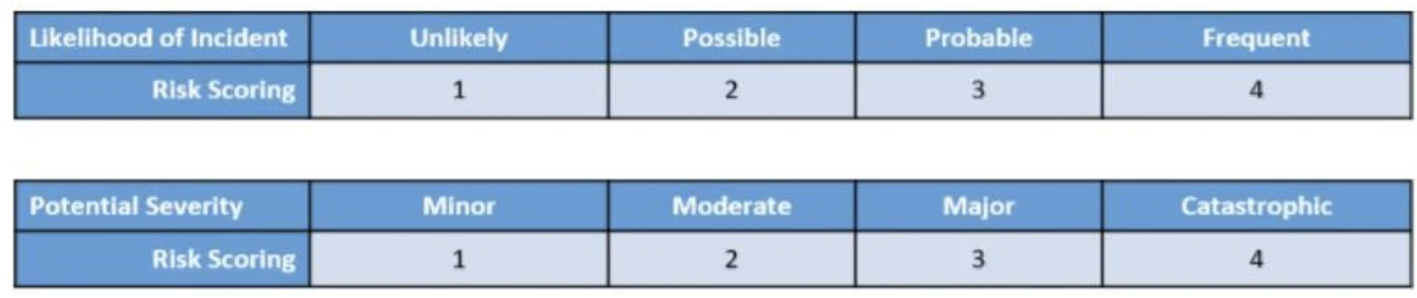
4. Implement Controls
Once you’ve determined which risks pose the greatest threat, you will need to decide what should be done to eliminate or reduce the risk.
Controls include measures like policies, procedures, training, tools or personal protective equipment that help manage risk. For example, a lockout/tagout procedure can help control the risk of injuries when equipment is undergoing maintenance.
It’s important that your control measures are specific. Vague, generic statements like “be aware” or “use PPE” are commonly seen on risk assessments and do nothing to make the work environment safer.
5. Review & Monitor
After you’ve implemented controls, it’s important to review and monitor them on a regular basis. Monitoring ensures that the controls are being properly implemented, and that they’re effective in mitigating the risks you’ve identified. It also helps determine if anything has changed that impacts your controls, or if there’s anything you may have overlooked.
Now, let’s look at another tool in the risk management toolkit — the risk register.

What is a Risk Register?
A risk register, also known as a risk registry or risk matrix, is a central record of all the risks you’ve identified across your organization.
Risk registers use a standardized scoring system to rank enterprise risks across thousands of observations.
The benefit of being able to quantify risks in this way is that you don’t have to take a “putting out fires” approach. You know which risks are most likely to occur and most significant, and can address them appropriately.
A risk register can be housed in a document, spreadsheet, or database — but the best way to keep track of an EHS risk register is inside risk management software.
Here’s an example of what a risk registry looks like:
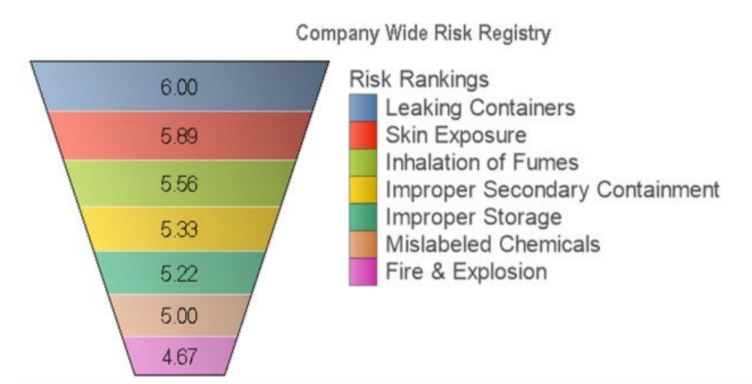
What is Risk Management Software?
Risk management software brings all of your risk data and activities together in one place, in order to create a clear picture of your company’s liabilities and opportunities.
Until very recently, EHS risk management was mostly a pencil-and-paper process. A handful of employees (usually supervisors or EHS leaders) would perform risk assessments to identify hazards like unguarded parts in machinery and improperly stored chemicals.
After the risk assessment, they would manually enter that data into spreadsheets. Often, there were different spreadsheets for different facilities or departments.
From there, the data in these spreadsheets had to be compiled into reports by hand — a process that could take weeks or months.
This resulted in a fragmented, outdated picture of the company’s risk profile. And there was no easy way to measure whether or not mitigation plans were actually working to reduce the company’s risks.
Here’s what a typical risk management process used to look like:
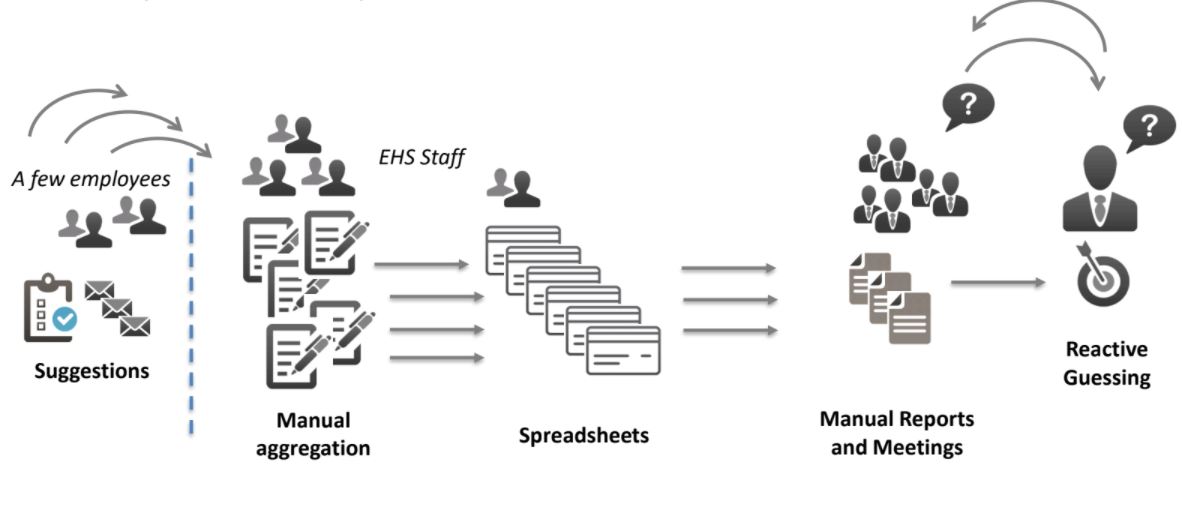
Compare that to this view of a modern risk management process that uses risk management software to connect data collection, analysis, reporting, and decision-making via a centralized platform:
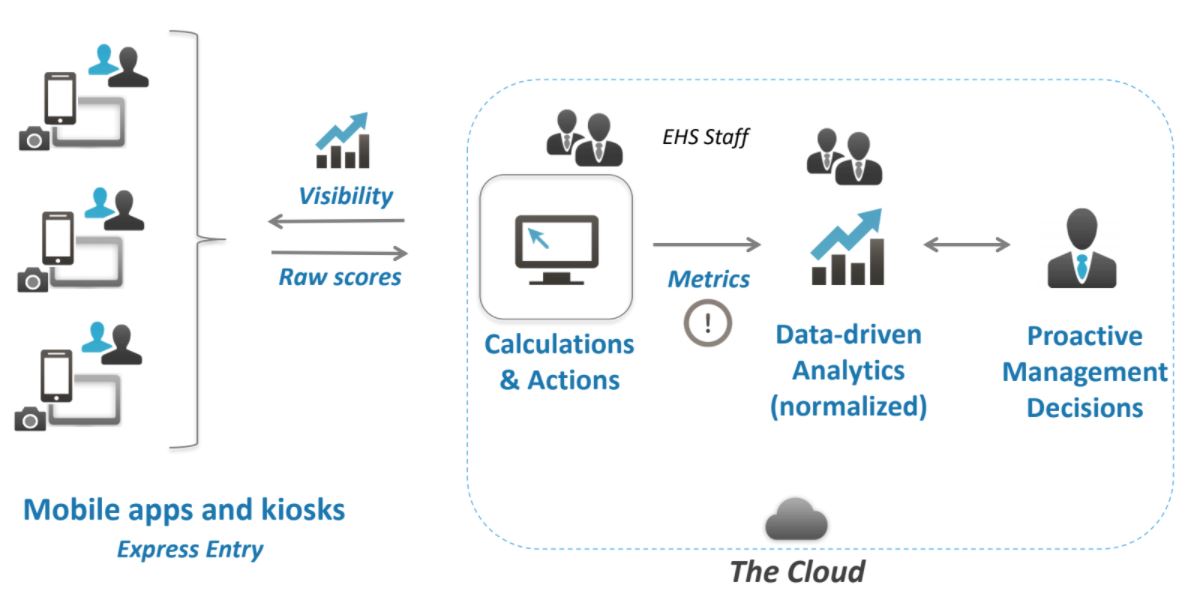
In this new model, high volumes of risk information are captured digitally, at the source. The data is entered directly into a central database, where the software performs calculations like risk scoring and triggers tasks or actions based on that information. And because the information is no longer siloed, management is able to see the whole picture and make timely, informed decisions.
Your Next Steps
Now that you’ve seen the ways software can help you improve your risk management processes, you might be ready to learn more about some of the solutions that are available. Our solutions team will walk you through the features you need to get the results you want. Request a demo today.