7 Tips for Effective Job Safety Analysis (JSA)
This article is part of our Back To Basics series, which highlights fundamental principles of environmental, health, and safety management. The series is written for EHS professionals new to this industry, as well as experienced pros who want to keep their skills fresh. A Job Safety Analysis (JSA) can feel like just another task on your to-do list. But if you do it right, you’ll see fewer injuries, better buy-in for your safety program, and less paperwork floating around on your desk.
Below, we’ll show you 5 tips for an effective job safety analysis. Even if you’ve been doing JSAs for years, these tips will help you to refine your process and potentially give you a fresh perspective on this critical task.
First, why is job safety analysis important?
A job safety analysis (JSA), also called a job hazard analysis (JHA), is a way to identify the dangers of specific tasks in order to reduce the risk of injury to workers.
It involves breaking down job tasks, identifying hazards at each step, and creating controls to keep workers safe while performing that task.
In addition to meeting OSHA requirements, JSAs can help you:
- Improve safety awareness
- Prevent injuries
- Simplify compliance with OSHA Hazard Assessment Requirements
- Improve your training program
- Increase worker productivity
- Reduce worker’s compensation costs
- Avoid OSHA violations
- Improve communication between workers and supervisors
In short: Smart safety managers know that time spent on JSAs is time well spent.
7 Job Safety Analysis (JSA) Tips
- Choose the right jobs to analyze
- Get workers involved
- Ask the right questions
- Standardize your JHA/JSA process
- Make use of images and video
- Give employees easy access to JSA information
- Keep it updated
1. Choose the right jobs to analyze
Let’s face it: Few organizations have the resources to complete a JSA for every single job they perform. What this means is that you’re going to have to get really good at prioritizing which jobs should be analyzed. So before you even grab your clipboard or iPad, it’s important to make sure you’ve selected the right job for your JSA.
In general, OSHA recommends prioritizing the following types of jobs for JSA:
- Jobs with the highest injury or illness rates;
- Jobs with the potential for severe injuries or illness;
- Jobs in which one error could lead to a severe accident;
- New jobs, or those that have undergone changes in processes and procedures;
- Complex enough to require written instructions.
2. Get workers involved
If you want to create an effective JSA, get your workers involved in the process. By inviting employee input on the job hazard analysis, safety managers and supervisors can gain buy-in and improve awareness about your safety program. And, perhaps more importantly, you may gain valuable safety insight you might never have developed on your own.
3. Ask the right questions
Of course, employees can only help you if they know what you’re looking for. As you walk through each step of the job, ask both open-ended and specific questions to drill down to potential hazards:
- Does this task involve lifting, pushing, or pulling?
- Is there a potential for slips, trips, or falls?
- Does the equipment present any potential hazards?
- Are there any pinch points or places body parts/clothing could get caught in the equipment?
- Is there exposure to extreme heat or cold?
- Are there loud noises or vibration?
- What potentially harmful substances or electrical hazards are involved?
4. Standardize your JHA/JSA process
One way to make sure you ask the right questions — no matter who’s conducting the JSA — is to standardize your process.
With an audit management software like Lisam ComplyStation, you can build a JSA template, save questions for re-use, and add logic to skip questions or trigger next steps. The process of running through a standard template or question set can bring to mind a few things you might not think of while creating a JSA in a hurry.
An added benefit: The process will get faster every time, so you’ll ultimately spend less time in the office preparing reports and more time in the field.
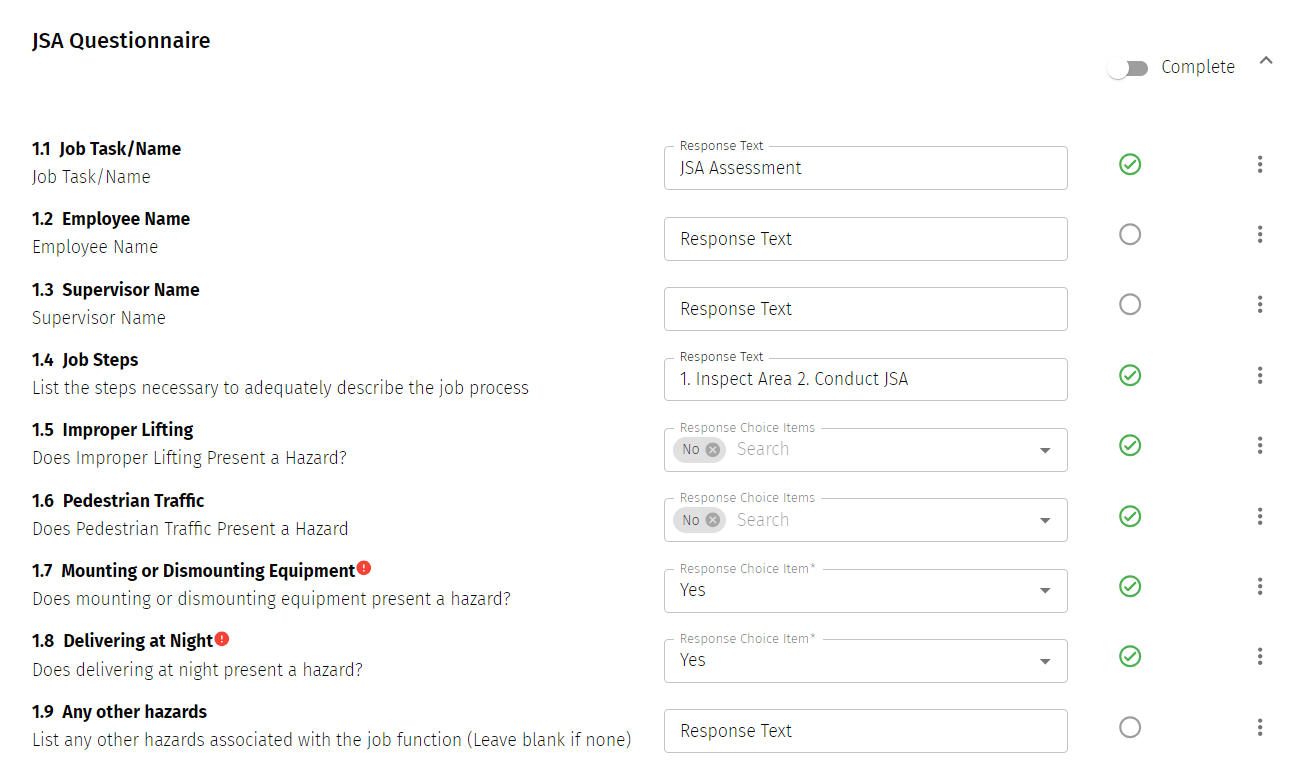
An example of a JSA checklist in ComplyStation.
5. Make use of images and video
Oftentimes it’s difficult to describe specific tasks or job processes in writing. But a picture, as the saying goes, is worth a thousand words. Adding images or video to your JSA can help illustrate potential hazards or safety principles more effectively. For instance, if your JSA mentions uneven concrete or a pinch point on a specific piece of equipment, you can simply snap a picture of the hazard and add it to your JSA form. This can make your JSA easier to understand. Not only that, but it provides workers with a quick reference at a glance.
6. Give employees easy access to JSA information
For your JSA to work, employees need easy access on the go — say, if they’re working on an oil rig and can’t get to a desktop computer.
Making your JSAs available on mobile (even offline) puts critical safety information at your workers’ fingertips. With a mobile audit tool, you can choose who sees what and keep everyone in the loop.
7. Keep it updated
Think of your JSA as a living document — one that needs to be reviewed and updated periodically.
Even if the job hasn’t changed, you might identify new hazards that you missed before. This is especially true if a near miss or accident occurs. You’ll want to review your JSA and ask:
- Did workers follow the JSA? If not, what additional training is needed?
- Are there new hazards that weren’t identified in the initial JSA?
- Do the hazard controls need to be changed or updated?
Audit management software makes it easy to update JSAs and notify need-to-know employees about important updates.
The final tip: don’t just read!
Go to your Lisam dashboard or current JSA form. Pick just one of the tips above to apply on your next JSA. Once you commit to creating great JSAs, we’re confident you’ll see fewer injuries and better buy-in for your safety program.
Next, learn how to standardize your inspections using Lisam ComplyStation.
Note: This article was originally published September 2017 and has been updated for freshness, accuracy, and comprehensiveness.
